Neck and Cervical Spine Anatomy
The vertebral bodies encase the spinal cord to provide protection. When stacked on top of each other, they form the spinal column which provides stability for the head and upper body. The spinal cord and the nerve exits are located within the spinal canal.
The intervertebral discs are located between the vertebral bodies. These discs cushion shock forces, acting as “shock absorbers”. The discs in conjunction with the vertebral joints facilitate motion by turning, stretching and bending of the neck.
The treatment goal of the prodisc C Total Disc Replacement is to restore the normal dynamic function of the spine and to significantly reduce pain.
The function of the spine is restored through the mechanism of action of the device. Pain reduction is achieved through the re-establishment of the disc height, and maintained by the prosthesis. The increase in height and the elimination of the herniated disc “opens” constricted nerve paths and the vertebral joints are restored to their physiological position.
Prior to the development of artificial discs the only surgical option was a fusion, in which adjacent vertebral bodies are “fused together” permanently using implants, bone chips and/or cages. The goal of prodisc C is to maintain mobility at the affected intervertebral disc and to reduce the extra loading on the adjacent intervertebral discs.
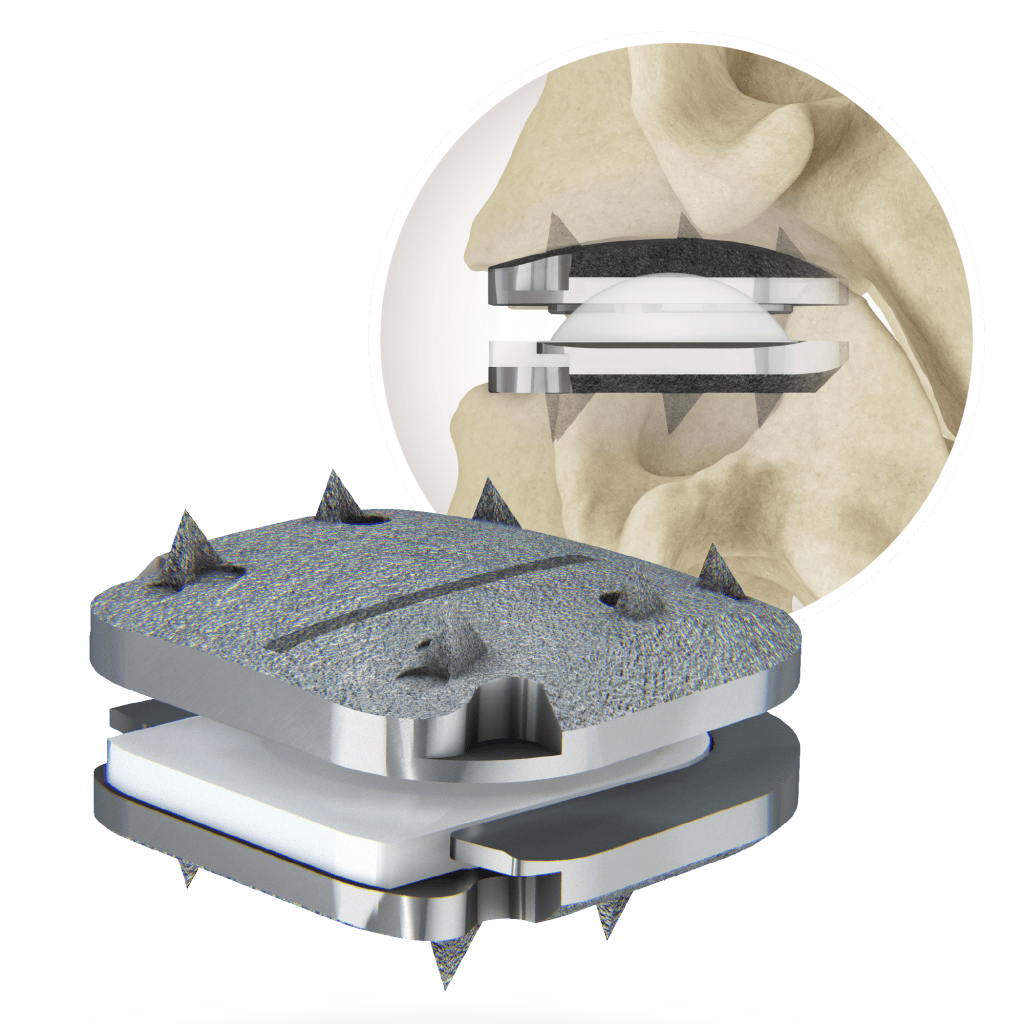
Degenerative disc disease can destabilize segments over time. In addition, performing the surgical discectomy is inherently destabilizing, as it involves the removal of the Anterior Longitudinal Ligament, the disc, and often, the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament. In the absence of these restricting structures, it is important for a disc replacement to have constraints in order to protect the facet joints
* L5, LD5, XL5 and XLD5 sizes allow 17.5° in flexion / extension and lateral bending.
The historical treatment for degenerative disc disease is to conduct an ACDF and fuse the joint. However, immobilizing a segment of the spine has been shown to increase the rate of adjacent-level degeneration. By enabling motion, prodisc is intended to decelerate adjacent level degeneration. A paper published on the results with the US IDE PMA clinical study on prodisc showed that, at seven years follow-up, patients had four times fewer reoperations of adjacent segments, compared to patients that received an ACDF.
1 Janssen ME, et al, ProDisc-C Total Disc Replacement Versus ACDF for Single-Level Symptomatic Cervical Disc Disease, JBJS, 2015, 97:1738-47.
